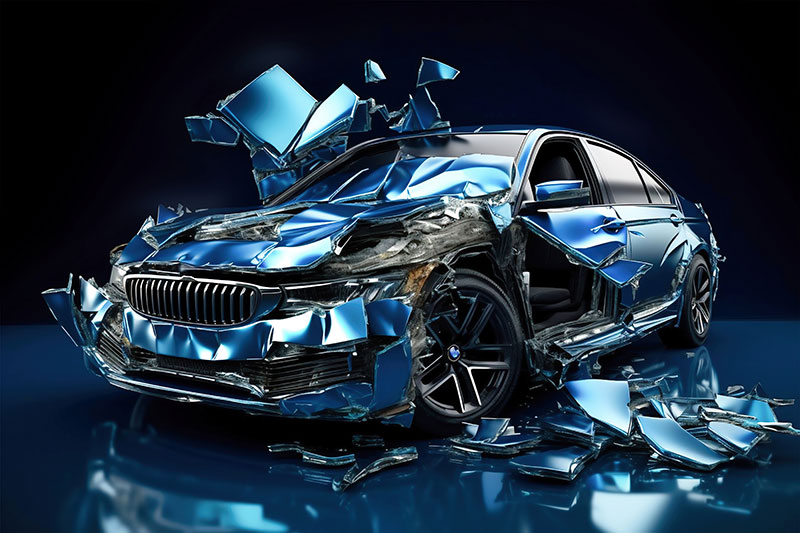
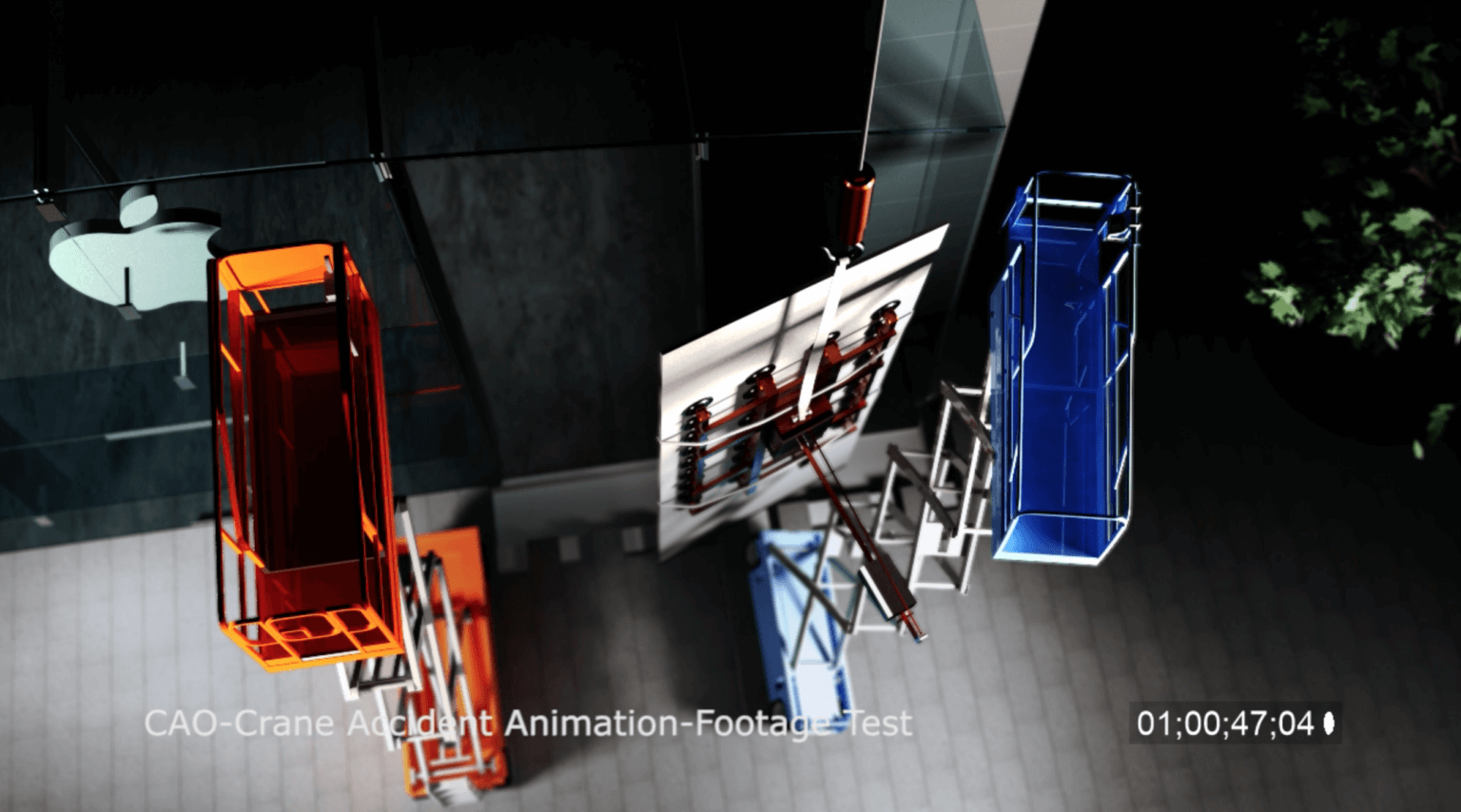
Forensic Animation
Around the year 2010, it was approximated that the animation industry had a value of about US$80 billion. However, by 2020, this worth had risen significantly to an estimated US$270 billion. Between 2004 and 2013, animated feature-length films demonstrated the highest profit margins (approximately 52%) compared to other genres within the film industry. As of the early 2020s, animation as both an art form and a business continues to flourish.
During this phase of the production process, animators manipulate the characters to enact every scene. Giulia's physical movements and facial gestures effectively communicate her unique traits and emotional states.
In the realm of 2D animation, characters are crafted or modified on a computer utilizing both 2D bitmap graphics and 2D vector graphics. This encompasses mechanized adaptations of conventional animation methods such as interpolated morphing, onion skinning, and interpolated rotoscoping. The applications of 2D animation span across various realms, including After Effects Animation, analog computer animation, Flash animation, and PowerPoint animation. Cinemagraphs are essentially static images that incorporate subtle animated elements in the form of a GIF file.